Bio-CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) or CBG (Compressed Biogas) is the purified and compressed form of biogas, with a methane content of around 92-98%. Bio CNG is emerging as a sustainable energy solution that not only replaces fossil fuels but also contributes to a cleaner planet.
So, is it just like natural gas? Not exactly. In fact, it’s better than natural gas and much less harmful to the environment.
How? To understand that, you first need to know what Bio-CNG is and how it’s produced.
What is Bio CNG?
Bio CNG is obtained by compressing Biogas, which is a naturally produced gas through the anaerobic decomposition of biomass like agricultural waste, animal manure, residue from agro-food industries, domestic organic waste, etc.

The main components in biogas are methane, carbon dioxide, and other gases in minute quantities like water vapour, oxygen, hydrocarbons, ammonia, etc.
Although it is a highly combustible gaseous fuel that releases heat and energy constituents like water vapour, hydrogen sulphide, and carbon dioxide, makes biogas is very unsuitable to be utilized as fuel.
Bio CNG fuel is a clean and renewable alternative to conventional fossil fuels. Although biogas is combustible, it needs purification to be used effectively as a sustainable energy solution. Bio CNG production is an innovative way to convert organic waste into clean and renewable energy.
The Role of Bio CNG Plants
Bio CNG plants play a vital role in the conversion of organic waste into clean energy. These facilities serve as hubs for the collection, processing, and purification of biogas derived from various sources.
Through advanced technologies such as biogas scrubbing, compression, and purification, Bio CNG plants ensure that the produced gas meets the quality standards required for use as a transportation fuel or for other industrial purposes. The use of Bio CNG fuel helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
The process of Bio CNG production helps reduce methane emissions and supports sustainable waste management.
By turning waste into energy, Bio CNG plants are a sustainable energy solution that supports both waste management and renewable energy generation.
What are the benefits of a Bio CNG Plant?
The adoption of Bio CNG technology offers multiple benefits, both environmental and economic:
Waste Management: Bio CNG plants help address the pressing issue of waste management by diverting organic waste from landfills and converting it into valuable energy.
Renewable Energy Source: Unlike fossil fuels, Bio CNG is a renewable energy source that reduces dependence on finite resources and mitigates greenhouse gas emissions.
Air Quality Improvement: The combustion of Bio CNG produces significantly fewer pollutants compared to conventional fuels, leading to improved air quality and reduced environmental degradation.
Economic Opportunities: Establishing Bio CNG plants creates job opportunities in waste collection, plant operation, and maintenance, contributing to local economic development.
Energy independence: By harnessing locally available organic waste, Bio CNG plants enhance energy security and reduce reliance on imported fuels.
What is the Process of Converting Biogas to Bio CNG?
Bio CNG is the purified and compressed form of biogas with around 92 – 98% of methane content. The purification of biogas is essential to increase its energy potential.
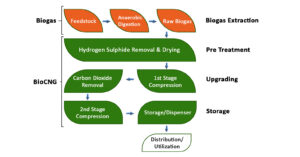
Although biogas purification can be done in various ways, these are the two most commonly used methods:
Water Scrubbing: This method involves compressing the biogas under pressure before exposing it to water. Carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S), which are more soluble in water than methane (CH4), dissolve in the water while methane rises to the top and is collected. The remaining liquid undergoes treatment to recover any remaining methane.
Pressure Swing Adsorption: In this technique, unwanted gases are captured by a vessel at high pressure. Methane is then collected from the top of the vessel, while the pressure is reduced to release carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), and oxygen (O2), similar to how fly paper sticks and unsticks when needed.
Why Choose Bio CNG Over CNG?
Choosing between Bio CNG and conventional CNG (compressed natural gas) involves considering various factors such as environmental impact, availability, and cost-effectiveness of the fuel.
| Aspect | Bio-CNG | Conventional CNG |
| Source | Derived from organic waste materials (renewable) | Extracted from fossil fuel reserves (non-renewable) |
| Carbon Footprint | Lower emissions due to recent carbon absorption | Higher emissions due to fossil fuel combustion |
| Waste Management | Provides a solution for organic waste disposal | Does not address organic waste management |
| Rural Development | Stimulates economic activities in rural areas | Limited impact on rural development |
Here are the reasons why you should choose bio-CNG over conventional CNG:
- Renewable source: Derived from organic waste, reducing reliance on finite fossil fuels.
- Reduced carbon footprint: Emission of lower levels of greenhouse gases due to recent carbon absorption by plants.
- Waste management solution: Converts organic waste into useful energy, reducing pollution and landfill usage.
- Potential for rural development: Stimulates economic activities in rural areas and improves living standards.
Future of Bio CNG Plants in India
- National Biogas and Manure Management Programme (NBMMP): Launched by the Ministry of Non-Renewable Energy, this program provides financial assistance and technical support to farmers and stakeholders for the establishment and operation of biogas or Bio CNG plants.
- National Clean Energy Fund (NCEF): This fund offers financial support for the development of clean energy technologies, including biogas.
- National Mission on Biogas and Organic Manure (NMBOM): The mission aims to popularise biogas as a clean and renewable energy source while also encouraging the use of organic manure in agriculture.
- Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE): Implementing various policies and schemes, the MNRE endeavours to promote renewable energy, including biogas and Bio CNG, across India.
- Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan (GOBAR-DHAN): This scheme targets the conversion of cattle dung and farm solid waste into Bio CNG (CBG) and compost, with plans to cover 700 projects nationwide.
Why is CNG Better Than Any Other Fuel?
CNG is better than many other fuels because it is cleaner, cheaper, and more efficient. It produces fewer harmful gases like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter compared to petrol or diesel, making it better for the environment and public health.
CNG is also more affordable, reduces fuel costs, and helps lower vehicle maintenance expenses due to cleaner engine operation.
Final Thought
In conclusion, Bio-CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) or CBG (Compressed Biogas) is a highly purified and compressed form of biogas, primarily composed of methane, obtained through the anaerobic decomposition of organic waste materials such as agricultural waste, animal manure, and domestic organic waste.
The future of Bio-CNG plants in India looks promising, supported by government initiatives which aim to popularize biogas as a clean and renewable energy source, reduce dependence on finite fossil fuels, and promote sustainable development practices. If you need any information or assistance with Bio CNG plants, you can contact us!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Question: What is the future of bio-CNG in India?
Answer: Bio-compressed natural gas (Bio-CNG) has the best potential in India as a cleaner alternative to CNG and LPG. It can be used in many industries, such as distilleries, sugar mills, starch factories, milk processing, and paper production.
Question: What is the government scheme for bio-CNG?
Answer: The main government scheme to promote bio-CNG in India is the SATAT (Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation) initiative. Launched by the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, this scheme supports the production and use of bio-CNG from waste and biomass.
Question: How is Bio-CNG different from CNG?
Answer: Both fuels mostly contain methane, but Bio-CNG is made from organic waste, while regular CNG is produced from fossil fuels. Bio-CNG is a renewable energy source, helps manage waste and produces fewer greenhouse gases. Bio CNG fuel is produced from organic waste, making it a key part of circular economy solutions.
Question: How is biogas converted to Bio-CNG?
Answer: Biogas is cleaned using methods like water scrubbing or pressure swing adsorption to remove unwanted gases. The cleaned gas, which has high methane content, is then compressed to make Bio-CNG.







